Hesperidin — разлика између измена
м razne ispravke; козметичке измене |
|||
| Ред 46: | Ред 46: | ||
}} |
}} |
||
'''Hesperidin''' je [[flavanon]]ski [[glikozid]] koji je izobilan u [[citrus]]nom voću. Njegova [[aglikon]]ska forma se naziva [[hesperetin]]. Ime potiče od [[Hesperide|hesperidnih]] nimfi iz Grčke mitologije. Za hesperidin se misli da učestvuje u odbrambenom mehanizmu [[biljka|biljki]]. Sudeći po ''[[in vitro]]'' ispitivanjima, on deluje kao [[antioksidans]].<ref>{{cite journal | |
'''Hesperidin''' je [[flavanon]]ski [[glikozid]] koji je izobilan u [[citrus]]nom voću. Njegova [[aglikon]]ska forma se naziva [[hesperetin]]. Ime potiče od [[Hesperide|hesperidnih]] nimfi iz Grčke mitologije. Za hesperidin se misli da učestvuje u odbrambenom mehanizmu [[biljka|biljki]]. Sudeći po ''[[in vitro]]'' ispitivanjima, on deluje kao [[antioksidans]].<ref>{{cite journal |vauthors=Hirata A, Murakami Y, Shoji M, Kadoma Y, Fujisawa S |title=Kinetics of radical-scavenging activity of hesperetin and hesperidin and their inhibitory activity on COX-2 expression |journal=Anticancer Res. |volume=25 |issue=5 |pages=3367–74 |year=2005 |pmid=16101151 }}</ref> |
||
Razna preliminarna ispitivanja indiciraju da on ima specifične farmaceutske osobine, mada nije potvrđeno da su one primenljive kod ljudi. Hesperidin redukuje novo [[holesterol]]a<ref>{{cite journal | |
Razna preliminarna ispitivanja indiciraju da on ima specifične farmaceutske osobine, mada nije potvrđeno da su one primenljive kod ljudi. Hesperidin redukuje novo [[holesterol]]a<ref>{{cite journal |vauthors=Monforte MT, Trovato A, Kirjavainen S, Forestieri AM, Galati EM, Lo Curto RB |title=Biological effects of hesperidin, a Citrus flavonoid. (note II): hypolipidemic activity on experimental hypercholesterolemia in rat |journal=Farmaco |volume=50 |issue=9 |pages=595–9 |year=1995 |month=September |pmid=7495469 }}</ref> i krvnog pritiska<ref>{{cite journal |author1=Ohtsuki K |author2=Abe A |author3=Mitsuzumi H |author4=''et al.'' |title=Glucosyl hesperidin improves serum cholesterol composition and inhibits hypertrophy in vasculature |journal=J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. |volume=49 |issue=6 |pages=447–50 |year=2003 |month=December |pmid=14974738 }}</ref> kod pacova. U jednoj studiji na miševima, velike doze hesperidina su snizile gubitak gustine kostiju.<ref>{{cite journal |author1=Chiba H |author2=Uehara M |author3=Wu J |author4=''et al.'' |title=Hesperidin, a citrus flavonoid, inhibits bone loss and decreases serum and hepatic lipids in ovariectomized mice |journal=J. Nutr. |volume=133 |issue=6 |pages=1892–7 |year=2003 |month=June |pmid=12771335 }}</ref> Jedna druga studija na životinjama je pokazala protektivne efekte protiv sepse.<ref>{{cite journal |doi=10.1248/bpb.27.679 |vauthors=Kawaguchi K, Kikuchi S, Hasunuma R, Maruyama H, Yoshikawa T, Kumazawa Y |title=A citrus flavonoid hesperidin suppresses infection-induced endotoxin shock in mice |journal=Biol. Pharm. Bull. |volume=27 |issue=5 |pages=679–83 |year=2004 |month=May |pmid=15133244 }}</ref> U ''in vitro'' i laboratorijskim istraživanjima, hesperidin pokazuje antiinflamatorno dejstvo.<ref>{{cite journal |vauthors=Emim JA, Oliveira AB, Lapa AJ |title=Pharmacological evaluation of the anti-inflammatory activity of a citrus bioflavonoid, hesperidin, and the isoflavonoids, duartin and claussequinone, in rats and mice |journal=J. Pharm. Pharmacol. |volume=46 |issue=2 |pages=118–22 |year=1994 |month=February |pmid=8021799 }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |vauthors=Galati EM, Monforte MT, Kirjavainen S, Forestieri AM, Trovato A, Tripodo MM |title=Biological effects of hesperidin, a citrus flavonoid. (Note I): antiinflammatory and analgesic activity |journal=Farmaco |volume=40 |issue=11 |pages=709–12 |year=1994 |month=November |pmid=7832973 }}</ref> Hesperidin je isto tako potencijalni [[sedativ]]. Moguće je da on deluje putem [[opioidni receptor|opioidnih]] ili [[Adenozinski receptor|adenozinskih]] receptora.<ref>{{cite journal |vauthors=Loscalzo LM, Wasowski C, Paladini AC, Marder M |title=Opioid receptors are involved in the sedative and antinociceptive effects of hesperidin as well as in its potentiation with benzodiazepines |journal=Eur. J. Pharmacol. |volume=580 |issue=3 |pages=306–13 |year=2008 |month=February |pmid=18048026 |doi=10.1016/j.ejphar.2007.11.011 }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |vauthors=Guzmán-Gutiérrez SL, Navarrete A |title=Pharmacological exploration of the sedative mechanism of hesperidin identified as the active principle of Citrus sinensis flowers |journal=Planta Med. |volume=75 |issue=4 |pages=295–301 |year=2009 |month=March |pmid=19219759 |doi=10.1055/s-0029-1185306 }}</ref> Hesperidin pokazuje izraženo antikancerno dejstvo protiv nekih ljudskih [[karcinom]]nih [[ćelijska kultura|ćelijskih linija]].<ref>-{Al-Ashaal HA, El-Sheltawy ST"Antioxidant capacity of hesperidin from citrus peel using electron spin resonance and cytotoxic activity against human carcinoma cell lines. ''Pharm Biol.'' 2011 Mar;49(3):276-82}-</ref> |
||
Deo ''in vitro'' rezultata je primenljiv samo na aglikonsku formu. Hesperidin takođe ima sposobnost penetracije [[krvno-moždana barijera|krvno moždane barijere]] u ''in vitro'' modelima.<ref>{{cite journal |doi=10.1046/j.1471-4159.2003.01652.x | |
Deo ''in vitro'' rezultata je primenljiv samo na aglikonsku formu. Hesperidin takođe ima sposobnost penetracije [[krvno-moždana barijera|krvno moždane barijere]] u ''in vitro'' modelima.<ref>{{cite journal |doi=10.1046/j.1471-4159.2003.01652.x |vauthors=Youdim KA, Dobbie MS, Kuhnle G, Proteggente AR, Abbott NJ, Rice-Evans C |title=Interaction between flavonoids and the blood-brain barrier: in vitro studies |journal=J. Neurochem. |volume=85 |issue=1 |pages=180–92 |year=2003 |month=April |pmid=12641740 }}</ref> |
||
== Reference == |
== Reference == |
||
Верзија на датум 24. октобар 2016. у 03:22
| |
| Nazivi | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC naziv
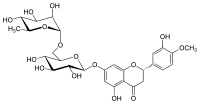
(2S)-5-hidroksi-2-(3-hidroksi-4-metoksifenil)-7-[(2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihidroksi-6-[[(2R,3R,4R,5R,6S)-3,4,5-trihidroksi-6-metiloksan-2-il]oksimetil]oksan-2-il]oksi-2,3-dihidrohromen-4-on
| |
| Identifikacija | |
3D model (Jmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.536 |
| UNII | |
| |
| Svojstva | |
| C28H34O15 | |
| Molarna masa | 610,57 g·mol−1 |
Ukoliko nije drugačije napomenuto, podaci se odnose na standardno stanje materijala (na 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Reference infokutije | |
Hesperidin je flavanonski glikozid koji je izobilan u citrusnom voću. Njegova aglikonska forma se naziva hesperetin. Ime potiče od hesperidnih nimfi iz Grčke mitologije. Za hesperidin se misli da učestvuje u odbrambenom mehanizmu biljki. Sudeći po in vitro ispitivanjima, on deluje kao antioksidans.[3]
Razna preliminarna ispitivanja indiciraju da on ima specifične farmaceutske osobine, mada nije potvrđeno da su one primenljive kod ljudi. Hesperidin redukuje novo holesterola[4] i krvnog pritiska[5] kod pacova. U jednoj studiji na miševima, velike doze hesperidina su snizile gubitak gustine kostiju.[6] Jedna druga studija na životinjama je pokazala protektivne efekte protiv sepse.[7] U in vitro i laboratorijskim istraživanjima, hesperidin pokazuje antiinflamatorno dejstvo.[8][9] Hesperidin je isto tako potencijalni sedativ. Moguće je da on deluje putem opioidnih ili adenozinskih receptora.[10][11] Hesperidin pokazuje izraženo antikancerno dejstvo protiv nekih ljudskih karcinomnih ćelijskih linija.[12]
Deo in vitro rezultata je primenljiv samo na aglikonsku formu. Hesperidin takođe ima sposobnost penetracije krvno moždane barijere u in vitro modelima.[13]
Reference
- ^ Li Q, Cheng T, Wang Y, Bryant SH (2010). „PubChem as a public resource for drug discovery.”. Drug Discov Today. 15 (23-24): 1052—7. PMID 20970519. doi:10.1016/j.drudis.2010.10.003.
- ^ Evan E. Bolton; Yanli Wang; Paul A. Thiessen; Stephen H. Bryant (2008). „Chapter 12 PubChem: Integrated Platform of Small Molecules and Biological Activities”. Annual Reports in Computational Chemistry. 4: 217—241. doi:10.1016/S1574-1400(08)00012-1.
- ^ Hirata A, Murakami Y, Shoji M, Kadoma Y, Fujisawa S (2005). „Kinetics of radical-scavenging activity of hesperetin and hesperidin and their inhibitory activity on COX-2 expression”. Anticancer Res. 25 (5): 3367—74. PMID 16101151.
- ^ Monforte MT, Trovato A, Kirjavainen S, Forestieri AM, Galati EM, Lo Curto RB (1995). „Biological effects of hesperidin, a Citrus flavonoid. (note II): hypolipidemic activity on experimental hypercholesterolemia in rat”. Farmaco. 50 (9): 595—9. PMID 7495469. Непознати параметар
|month=игнорисан (помоћ) - ^ Ohtsuki K; Abe A; Mitsuzumi H; et al. (2003). „Glucosyl hesperidin improves serum cholesterol composition and inhibits hypertrophy in vasculature”. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 49 (6): 447—50. PMID 14974738. Непознати параметар
|month=игнорисан (помоћ) - ^ Chiba H; Uehara M; Wu J; et al. (2003). „Hesperidin, a citrus flavonoid, inhibits bone loss and decreases serum and hepatic lipids in ovariectomized mice”. J. Nutr. 133 (6): 1892—7. PMID 12771335. Непознати параметар
|month=игнорисан (помоћ) - ^ Kawaguchi K, Kikuchi S, Hasunuma R, Maruyama H, Yoshikawa T, Kumazawa Y (2004). „A citrus flavonoid hesperidin suppresses infection-induced endotoxin shock in mice”. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 27 (5): 679—83. PMID 15133244. doi:10.1248/bpb.27.679. Непознати параметар
|month=игнорисан (помоћ) - ^ Emim JA, Oliveira AB, Lapa AJ (1994). „Pharmacological evaluation of the anti-inflammatory activity of a citrus bioflavonoid, hesperidin, and the isoflavonoids, duartin and claussequinone, in rats and mice”. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 46 (2): 118—22. PMID 8021799. Непознати параметар
|month=игнорисан (помоћ) - ^ Galati EM, Monforte MT, Kirjavainen S, Forestieri AM, Trovato A, Tripodo MM (1994). „Biological effects of hesperidin, a citrus flavonoid. (Note I): antiinflammatory and analgesic activity”. Farmaco. 40 (11): 709—12. PMID 7832973. Непознати параметар
|month=игнорисан (помоћ) - ^ Loscalzo LM, Wasowski C, Paladini AC, Marder M (2008). „Opioid receptors are involved in the sedative and antinociceptive effects of hesperidin as well as in its potentiation with benzodiazepines”. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 580 (3): 306—13. PMID 18048026. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2007.11.011. Непознати параметар
|month=игнорисан (помоћ) - ^ Guzmán-Gutiérrez SL, Navarrete A (2009). „Pharmacological exploration of the sedative mechanism of hesperidin identified as the active principle of Citrus sinensis flowers”. Planta Med. 75 (4): 295—301. PMID 19219759. doi:10.1055/s-0029-1185306. Непознати параметар
|month=игнорисан (помоћ) - ^ Al-Ashaal HA, El-Sheltawy ST"Antioxidant capacity of hesperidin from citrus peel using electron spin resonance and cytotoxic activity against human carcinoma cell lines. Pharm Biol. 2011 Mar;49(3):276-82
- ^ Youdim KA, Dobbie MS, Kuhnle G, Proteggente AR, Abbott NJ, Rice-Evans C (2003). „Interaction between flavonoids and the blood-brain barrier: in vitro studies”. J. Neurochem. 85 (1): 180—92. PMID 12641740. doi:10.1046/j.1471-4159.2003.01652.x. Непознати параметар
|month=игнорисан (помоћ)
