Α-Aminoadipatni put — разлика између измена
. |
(нема разлике)
|
Верзија на датум 21. децембар 2023. у 14:14
Један корисник управо ради на овом чланку. Молимо остале кориснике да му допусте да заврши са радом. Ако имате коментаре и питања у вези са чланком, користите страницу за разговор.
Хвала на стрпљењу. Када радови буду завршени, овај шаблон ће бити уклоњен. Напомене
|
α-Aminoadipatni put je biohemijski put for the synthesis of the amino acid L-lysine. In the eukaryotes, this pathway is unique to the higher fungi (containing chitin in their cell walls) and the euglenids.[1] It has also been reported from bacteria of the genus Thermus.[2]
Pregled puta
Homocitrate is initially synthesised from acetyl-CoA and 2-oxoglutarate by homocitrate synthase. This is then converted to homoaconitate by homoaconitase and then to homoisocitrate by homoisocitrate dehydrogenase. A nitrogen atom is added from glutamate by aminoadipate aminotransferase to form the α-aminoadipate from which this pathway gets its name. This is then reduced by aminoadipate reductase via an acyl-enzyme intermediate to a semialdehyde. Reaction with glutamate by one class of saccharopine dehydrogenase yields saccharopine which is then cleaved by a second saccharopine dehydrogenase to yield lysine and oxoglutarate.[3]
α-Aminoadipinska kiselina
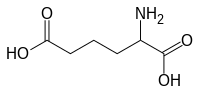
| |
| Nazivi | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC naziv
2-Aminohexanedioic acid
| |
| Drugi nazivi
2-Aminoadipic acid
| |
| Идентификација | |
3Д модел (Jmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| MeSH | 2-Aminoadipic+Acid |
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Svojstva | |
| C6H11NO4 | |
| Molarna masa | 161,156 g/mol |
| Agregatno stanje | Crystalline |
| Gustina | 1,333 g/mL |
| Tačka topljenja | 196 °C (385 °F; 469 K) |
| Tačka ključanja | 364 °C (687 °F; 637 K) |
| Opasnosti | |
| Opasnost u toku rada | Irritant |
Ukoliko nije drugačije napomenuto, podaci se odnose na standardno stanje materijala (na 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Reference infokutije | |
α-Aminoadipinska kiselina je conjugate acid of α-aminoadipate, the latter of which is the prevalent form at physiological pH. A 2013 study identified α-Aminoadipic acid (2-aminoadipic acid) as a novel predictor of the development of diabetes and suggested that it is a potential modulator of glucose homeostasis in humans.[6]
Reference
- ^ Zabriskie TM, Jackson MD (2000). „Lysine biosynthesis and metabolism in fungi”. Natural Product Reports. 17 (1): 85—97. PMID 10714900. doi:10.1039/a801345d.
- ^ Kosuge T, Hoshino T (1999). „The α-aminoadipate pathway for lysine biosynthesis is widely distributed among Thermus strains”. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering. 88 (6): 672—5. PMID 16232683. doi:10.1016/S1389-1723(00)87099-1.
- ^ Xu H, Andi B, Qian J, West AH, Cook PF (2006). „The α-aminoadipate pathway for lysine biosynthesis in fungi”. Cell Biochemistry and Biophysics. 46 (1): 43—64. PMID 16943623. S2CID 22370361. doi:10.1385/CBB:46:1:43.
- ^ Li Q, Cheng T, Wang Y, Bryant SH (2010). „PubChem as a public resource for drug discovery.”. Drug Discov Today. 15 (23-24): 1052—7. PMID 20970519. doi:10.1016/j.drudis.2010.10.003.
- ^ Evan E. Bolton; Yanli Wang; Paul A. Thiessen; Stephen H. Bryant (2008). „Chapter 12 PubChem: Integrated Platform of Small Molecules and Biological Activities”. Annual Reports in Computational Chemistry. 4: 217—241. doi:10.1016/S1574-1400(08)00012-1.
- ^ Wang TJ, Ngo D, Psychogios N, Dejam A, Larson MG, Vasan RS, Ghorbani A, O'Sullivan J, Cheng S, Rhee EP, Sinha S, McCabe E, Fox CS, O'Donnell CJ, Ho JE, Florez JC, Magnusson M, Pierce KA, Souza AL, Yu Y, Carter C, Light PE, Melander O, Clish CB, Gerszten RE (2013). „2-Aminoadipic acid is a biomarker for diabetes risk”. Journal of Clinical Investigation. 123 (10): 4309—4317. PMC 3784523
 . PMID 24091325. doi:10.1172/JCI64801.
. PMID 24091325. doi:10.1172/JCI64801.
