Veštačka neuronska mreža — разлика између измена
. |
(нема разлике)
|
Верзија на датум 7. мај 2018. у 08:55
Један корисник управо ради на овом чланку. Молимо остале кориснике да му допусте да заврши са радом. Ако имате коментаре и питања у вези са чланком, користите страницу за разговор.
Хвала на стрпљењу. Када радови буду завршени, овај шаблон ће бити уклоњен. Напомене
|
Veštačke neuronske mreže (engl. Artificial neural networks - ANN) ili konektivni sistemi su računarski sistemi koji donekle inspirisani biologiškim neuronskim mrežama od kojih su sačinjeni životinjski mozgovi.[1] Such systems "learn" (i.e. progressively improve performance on) tasks by considering examples, generally without task-specific programming. For example, in image recognition, they might learn to identify images that contain cats by analyzing example images that have been manually labeled as "cat" or "no cat" and using the results to identify cats in other images. They do this without any a priori knowledge about cats, e.g., that they have fur, tails, whiskers and cat-like faces. Instead, they evolve their own set of relevant characteristics from the learning material that they process.
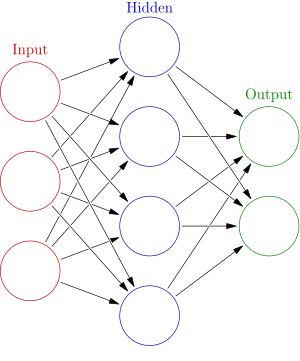
An ANN is based on a collection of connected units or nodes called artificial neurons (a simplified version of biological neurons in an animal brain). Each connection (a simplified version of a synapse) between artificial neurons can transmit a signal from one to another. The artificial neuron that receives the signal can process it and then signal artificial neurons connected to it.
In common ANN implementations, the signal at a connection between artificial neurons is a real number, and the output of each artificial neuron is calculated by a non-linear function of the sum of its inputs. Artificial neurons and connections typically have a weight that adjusts as learning proceeds. The weight increases or decreases the strength of the signal at a connection. Artificial neurons may have a threshold such that only if the aggregate signal crosses that threshold is the signal sent. Typically, artificial neurons are organized in layers. Different layers may perform different kinds of transformations on their inputs. Signals travel from the first (input), to the last (output) layer, possibly after traversing the layers multiple times.
The original goal of the ANN approach was to solve problems in the same way that a human brain would. However, over time, attention focused on matching specific tasks, leading to deviations from biology. ANNs have been used on a variety of tasks, including computer vision, speech recognition, machine translation, social network filtering, playing board and video games and medical diagnosis.
Reference
- ^ „Artificial Neural Networks as Models of Neural Information Processing | Frontiers Research Topic” (на језику: енглески). Приступљено 2018-02-20.
Literatura
- Bhadeshia H. K. D. H. (1999). „Neural Networks in Materials Science” (PDF). ISIJ International. 39 (10): 966—979. doi:10.2355/isijinternational.39.966.
- M., Bishop, Christopher (1995). Neural networks for pattern recognition. Clarendon Press. ISBN 0198538499. OCLC 33101074.
- Cybenko, G.V. (2006). „Approximation by Superpositions of a Sigmoidal function”. Ур.: van Schuppen, Jan H. Mathematics of Control, Signals, and Systems. Springer International. стр. 303—314. PDF
- Dewdney, A. K. (1997). Yes, we have no neutrons : an eye-opening tour through the twists and turns of bad science. New York: Wiley. ISBN 9780471108061. OCLC 35558945.
- Duda, Richard O.; Hart, Peter Elliot; Stork, David G. (2001). Pattern classification (2 изд.). Wiley. ISBN 0471056693. OCLC 41347061.
- Egmont-Petersen, M.; de Ridder, D.; Handels, H. (2002). „Image processing with neural networks – a review”. Pattern Recognition. 35 (10): 2279—2301. doi:10.1016/S0031-3203(01)00178-9.
- Gurney, Kevin (1997). An introduction to neural networks. UCL Press. ISBN 1857286731. OCLC 37875698.
- Haykin, Simon S. (1999). Neural networks : a comprehensive foundation. Prentice Hall. ISBN 0132733501. OCLC 38908586.
- Fahlman, S.; Lebiere, C (1991). „The Cascade-Correlation Learning Architecture” (PDF). created for National Science Foundation, Contract Number EET-8716324, and Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DOD), ARPA Order No. 4976 under Contract F33615-87-C-1499.
- Hertz, J.; Palmer, Richard G.; Krogh, Anders S. (1991). Introduction to the theory of neural computation. Addison-Wesley. ISBN 0201515601. OCLC 21522159.
- Lawrence, Jeanette (1994). Introduction to neural networks : design, theory and applications. California Scientific Software. ISBN 1883157005. OCLC 32179420.
- Information theory, inference, and learning algorithms. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9780521642989. OCLC 52377690.
- MacKay, David, J.C. (2003). Information Theory, Inference, and Learning Algorithms (PDF). Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9780521642989.
- Masters,, Timothy (1994). Signal and image processing with neural networks : a C++ sourcebook. J. Wiley. ISBN 0471049638. OCLC 29877717.
- Ripley, Brian D. (2007). Pattern Recognition and Neural Networks. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-71770-0.
- Siegelmann, H.T.; Sontag, Eduardo D. (1994). „Analog computation via neural networks” (PDF). Theoretical Computer Science. 131 (2): 331—360. doi:10.1016/0304-3975(94)90178-3.
- Smith, Murray (1993). Neural networks for statistical modeling. Van Nostrand Reinhold. ISBN 0442013108. OCLC 27145760.
- Wasserman, Philip D. (1993). Advanced methods in neural computing. Van Nostrand Reinhold. ISBN 0442004613. OCLC 27429729.
- Kruse, Rudolf,; Borgelt, Christian; Klawonn, F.; Moewes, Christian; Steinbrecher, Matthias; Held,, Pascal (2013). Computational intelligence : a methodological introduction. Springer. ISBN 9781447150121. OCLC 837524179.
- Borgelt,, Christian (2003). Neuro-Fuzzy-Systeme : von den Grundlagen künstlicher Neuronaler Netze zur Kopplung mit Fuzzy-Systemen. Vieweg. ISBN 9783528252656. OCLC 76538146.
Spoljašnje veze
- A brief introduction to Neural Networks (PDF), illustrated 250p textbook covering the common kinds of neural networks (CC license).
- -{An Introduction to Deep Neural Networks.
- A Tutorial of Neural Network in Excel.
- MIT course on Neural Networks на сајту YouTube
- A Concise Introduction to Machine Learning with Artificial Neural Networks
- Neural Networks for Machine Learning - a course by Geoffrey Hinton
- Deep Learning
