Tkivna transglutaminaza — разлика између измена
Нова страница: {{rut}}{{PBB|geneid=7052}} {{Infobox Enzim-lat | Name = Protein-glutamine gamma-glutamyltransferase | EC_number = 2.3.2.13 | CAS_number = 80146-85-6 | IUBMB_EC_number= … |
(нема разлике)
|
Верзија на датум 28. септембар 2013. у 18:20
Један корисник управо ради на овом чланку. Молимо остале кориснике да му допусте да заврши са радом. Ако имате коментаре и питања у вези са чланком, користите страницу за разговор.
Хвала на стрпљењу. Када радови буду завршени, овај шаблон ће бити уклоњен. Напомене
|
| Transglutaminaza 2 (C polipeptid, protein-glutamin-gama-glutamiltransferaza) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||
| Dostupne strukture | |||||||||||
| 1KV3, 2Q3Z, 3LY6, 3S3J, 3S3P, 3S3S | |||||||||||
| Identifikatori | |||||||||||
| Simboli | TGM2; G-ALPHA-h; GNAH; TG2; TGC | ||||||||||
| Vanjski ID | OMIM: 190196 MGI: 98731 HomoloGene: 3391 GeneCards: TGM2 Gene | ||||||||||
| EC broj | 2.3.2.13 | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| Pregled RNK izražavanja | |||||||||||
 | |||||||||||
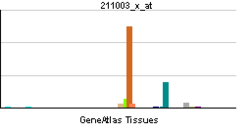 | |||||||||||
 | |||||||||||
| podaci | |||||||||||
| Ortolozi | |||||||||||
| Vrsta | Čovek | Miš | |||||||||
| Entrez | 7052 | 21817 | |||||||||
| Ensembl | ENSG00000198959 | ENSMUSG00000037820 | |||||||||
| UniProt | P21980 | P21981 | |||||||||
| RefSeq (mRNA) | NM_004613 | NM_009373 | |||||||||
| RefSeq (protein) | NP_004604 | NP_033399 | |||||||||
| Lokacija (UCSC) |
Chr 20: 36.76 - 36.79 Mb |
Chr 2: 158.12 - 158.15 Mb | |||||||||
| PubMed pretraga | [1] | [2] | |||||||||
| Protein-glutamine gamma-glutamyltransferase | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifikatori | |||||||||
| EC broj | 2.3.2.13 | ||||||||
| CAS broj | 80146-85-6 | ||||||||
| Baze podataka | |||||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz pregled | ||||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA pristup | ||||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme pregled | ||||||||
| KEGG | KEGG pristup | ||||||||
| MetaCyc | metabolički put | ||||||||
| PRIAM | profil | ||||||||
| Strukture PBP | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBj PDBsum | ||||||||
| Ontologija gena | AmiGO / EGO | ||||||||
| |||||||||
Tkivna transglutaminaza (tTG, TG2) je 78-kDa, od kalcijuma zavisni enzim (EC 2.3.2.13) iz familije γ-glutamiltransferaza (transglutaminaza).[1][2] Poput drugih transglutaminaza, it crosslinks proteins between an ε-amino group of a lysine residue and a γ-carboxamide group of glutamine residue, creating an inter- or intramolecular bond that is highly resistant to proteolysis (protein degradation). Aside from its crosslinking function, tTG catalyzes other types of reactions including deamidation, GTP-binding/hydrolyzing, and isopeptidase activities.[3] Unlike other members of the transglutaminase family, tTG can be found both in the intracellular and the extracellular spaces of various types of tissues and is found in many different organs including the heart, the liver, and the small intestine. Intracellular tTG is abundant in the cytosol but smaller amounts can also be found in the nucleus and the mitochondria.[2] Intracellular tTG is thought to play an important role in apoptosis.[4] In the extracellular space, tTG binds to proteins of the extracellular matrix (ECM),[5] binding particularly tightly to fibronectin.[6] Extracellular tTG has been linked to cell adhesion, ECM stabilization, wound healing, receptor signaling, cellular proliferation, and cellular motility.[2]
tTG is particularly notable for being the autoantigen in coeliac disease, a lifelong illness in which the consumption of dietary gluten causes a pathological immune response resulting in the inflammation of the small intestine and subsequent villous atrophy.[7][8][9]
Reference
- ^ Király R, Demény M, Fésüs L (2011). „Protein transamidation by transglutaminase 2 in cells: a disputed Ca2+-dependent action of a multifunctional protein”. FEBS J. 278 (24): 4717—39. PMID 21902809. doi:10.1111/j.1742-4658.2011.08345.x. Непознати параметар
|month=игнорисан (помоћ) - ^ а б в Klöck C, Diraimondo TR, Khosla C (2012). „Role of transglutaminase 2 in celiac disease pathogenesis”. Semin Immunopathol. 34 (4): 513—22. PMID 22437759. doi:10.1007/s00281-012-0305-0. Непознати параметар
|month=игнорисан (помоћ) - ^ Facchiano F, Facchiano A, Facchiano AM (2006). „The role of transglutaminase-2 and its substrates in human diseases”. Front. Biosci. 11: 1758—73. PMID 16368554. doi:10.2741/1921.
- ^ McConkey DJ, Orrenius S (1997). „The role of calcium in the regulation of apoptosis”. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 239 (2): 357—66. PMID 9344835. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1997.7409. Непознати параметар
|month=игнорисан (помоћ) - ^ Lortat-Jacob H, Burhan I, Scarpellini A, Thomas A, Imberty A, Vivès RR, Johnson T, Gutierrez A, Verderio EA (2012). „Transglutaminase-2 interaction with heparin: identification of a heparin binding site that regulates cell adhesion to fibronectin-transglutaminase-2 matrix”. J. Biol. Chem. 287 (22): 18005—17. PMC 3365763
 . PMID 22442151. doi:10.1074/jbc.M111.337089. Непознати параметар
. PMID 22442151. doi:10.1074/jbc.M111.337089. Непознати параметар |month=игнорисан (помоћ) - ^ Akimov SS, Krylov D, Fleischman LF, Belkin AM (2000). „Tissue transglutaminase is an integrin-binding adhesion coreceptor for fibronectin”. J. Cell Biol. 148 (4): 825—38. PMC 2169362
 . PMID 10684262. doi:10.1083/jcb.148.4.825. Непознати параметар
. PMID 10684262. doi:10.1083/jcb.148.4.825. Непознати параметар |month=игнорисан (помоћ) - ^ Griffin M, Casadio R, Bergamini CM (2002). „Transglutaminases: nature's biological glues”. Biochem. J. 368 (Pt 2): 377—96. PMC 1223021
 . PMID 12366374. doi:10.1042/BJ20021234. Непознати параметар
. PMID 12366374. doi:10.1042/BJ20021234. Непознати параметар |month=игнорисан (помоћ) - ^ Diraimondo TR, Klöck C, Khosla C (2012). „Interferon-γ activates transglutaminase 2 via a phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase-dependent pathway: implications for celiac sprue therapy”. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 341 (1): 104—14. PMC 3310700
 . PMID 22228808. doi:10.1124/jpet.111.187385. Непознати параметар
. PMID 22228808. doi:10.1124/jpet.111.187385. Непознати параметар |month=игнорисан (помоћ) - ^ Di Sabatino A, Vanoli A, Giuffrida P, Luinetti O, Solcia E, Corazza GR (2012). „The function of tissue transglutaminase in celiac disease”. Autoimmun Rev. 11 (10): 746—53. PMID 22326684. doi:10.1016/j.autrev.2012.01.007. Непознати параметар
|month=игнорисан (помоћ)
Spoljašnje veze
- Endomysial antibodies
- A collection of substrates and interaction partners of TG2 is accessible in the TRANSDAB, an interactive transglutaminase substrate database.

