Балтичко море — разлика између измена
мНема описа измене |
. |
||
| Ред 1: | Ред 1: | ||
[[Датотека:Baltic Sea map.png|мини|десно|250п|Балтик]] |
|||
{{bez_izvora}} |
|||
[[Датотека: |
[[Датотека:BalticSea March2000 NASA-S2000084115409 md.jpg|мини|250п|Сателитски снимак Балтика]] |
||
{{рут}} |
|||
[[Датотека:BalticSea March2000 NASA-S2000084115409 md.jpg|мини|280п|Сателитски снимак Балтика]] |
|||
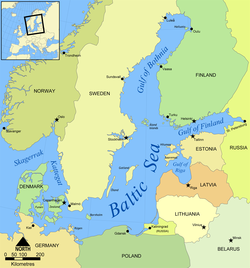
'''Балтичко море''' (краће '''Балтик'''), налази се на северу [[Европа|Европе]] и са [[Северно море|Северним морем]] повезано је тесним [[мореуз]]има: [[Сунда]], [[Велики Белт]], [[Мали Белт]], [[Скагерак]], [[Категат]] и [[Килски канал|Килским каналом]]. Назива се и као '''Источно море''' и '''Западно море'''. Оно запљускује [[Обала|обале]] [[Скандинавско полуострво|Скандинавског полуострва]], већег броја [[Држава|земаља]] [[Источна Европа|источне]], [[Северна Европа|северне]] и [[Средња Европа|централне Европе]]. Због његове велике површине (422.300 -{[[km²]]}-) и лоше повезаности са Северним морем-што онемогућава размену [[Вода|воде]], а великог прилива [[Слатка вода|слатке воде]] ово [[море]] је једно од мора са најнижим [[салинитет]]ом на [[свет]]у. |
'''Балтичко море''' (краће '''Балтик'''), налази се на северу [[Европа|Европе]] и са [[Северно море|Северним морем]] повезано је тесним [[мореуз]]има: [[Сунда]], [[Велики Белт]], [[Мали Белт]], [[Скагерак]], [[Категат]] и [[Килски канал|Килским каналом]]. Назива се и као '''Источно море''' и '''Западно море'''. Оно запљускује [[Обала|обале]] [[Скандинавско полуострво|Скандинавског полуострва]], већег броја [[Држава|земаља]] [[Источна Европа|источне]], [[Северна Европа|северне]] и [[Средња Европа|централне Европе]].<ref>{{cite web|title=Coalition Clean Baltic |url=http://www.ccb.se/newsletters/2005/07/map_final.jpg |accessdate=5 July 2013 |deadurl=yes |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20130602044612/http://www.ccb.se/newsletters/2005/07/map_final.jpg |archivedate=2 June 2013 }}</ref> Због његове велике површине (422.300 -{[[km²]]}-) и лоше повезаности са Северним морем-што онемогућава размену [[Вода|воде]], а великог прилива [[Слатка вода|слатке воде]] ово [[море]] је једно од мора са најнижим [[салинитет]]ом на [[свет]]у. |
||
Највећа дубина Балтичког мора износи 459 -{[[Метар|m]]}-. Велики [[залив]]и су: [[Ботнијски залив|Ботнички залив]], [[Фински залив]], [[Ришки залив]], [[Курски залив|Куронски залив]], [[Гдањски залив]], [[Шћећински залив]], [[Либечки залив]] и [[Килски залив]]. |
Највећа дубина Балтичког мора износи 459 -{[[Метар|m]]}-. Велики [[залив]]и су: [[Ботнијски залив|Ботнички залив]], [[Фински залив]], [[Ришки залив]], [[Курски залив|Куронски залив]], [[Гдањски залив]], [[Шћећински залив]], [[Либечки залив]] и [[Килски залив]]. |
||
== Дефиниције == |
|||
[[Датотека:Belte inter.png|thumb|250px|Дански теснаци и југозападно Балтичко море]] |
|||
'''Администрација''' |
|||
[[Хелсиншка конвенција о заштити морске средине подручја Балтичког мора]] обухвата Балтичко море и [[Категат]], без називања Категата делом Балтичког мора, „За потребе ове конвенције „подручје Балтичког мора” је Балтичко море и улаз у Балтичко море, ограничено паралелом Скава у Скагераку на 57° 44,43'С.”<ref>[http://www.helcom.fi/Documents/About%20us/Convention%20and%20commitments/Helsinki%20Convention/ Text of Helsinki Convention]</ref> |
|||
'''Историја саобраћаја''' |
|||
Историјски Данско краљевство је наплаћивало бродовим пролаз кроз теснаце на граници између океана и копном окруженог Балтичког мора. Наплата је вршена у [[Ересунд]]у код [[Кронборг|Кронборшког]] дворца у близини [[Хелсингер]], у [[Great Belt|Великом Белту]] код [[Ниборг]]а. У [[Little Belt]], the site of intake was moved to [[Fredericia]], after that stronghold had been built. The narrowest part of Little Belt is the "Middelfart Sund" near [[Middelfart]].<ref>[http://de.academic.ru/dic.nsf/pierer/66040/Sundzoll Pierers Universal-Lexikon, (a German encyclopedia from 1857–1865, automatic transcription of little quality): Sundzoll (Sound Dues )]</ref> |
|||
'''Океанографија''' |
|||
Geographers widely agree that the preferred physical border of the Baltic is a line drawn through the southern Danish islands, [[Drogden-Sill]] and [[Langeland]].<ref>[http://www.io-warnemuende.de/Antworten_Fragen_zum_Meer.html?frage=49 Leibniz-Institut für Ostseeforschung Warnemünde: "Gehört das Kattegatt noch zur Ostsee" (Is the Kattegat a part of the Baltic Sea?)]</ref> The Drogden Sill is situated north of [[Køge Bugt]] and connects [[Dragør]] in the south of [[Copenhagen]] to [[Malmö]]; it is used by the [[Øresund Bridge]], including the ''Drogden Tunnel''. By this definition, the [[Danish Straits]] are part of the entrance, but the [[Bay of Mecklenburg]] and the [[Bay of Kiel]] are parts of the Baltic Sea. |
|||
Another usual border is the line between [[Falsterbo]], Sweden and [[Stevns Klint]], Denmark, as this is the southern border of [[Øresund]]. It's also the border between the shallow southern Øresund (with a typical depth of 5–10 meters only) and notably deeper water. |
|||
'''Хидрографија и биологија''' |
|||
[[Drogden]] Sill (depth of {{convert|7|m|abbr=on}}) sets a limit to Øresund and [[Darss]] Sill (depth of {{convert|18|m|abbr=on}}), and a limit to the Belt Sea.<ref>[https://www.kemi.se/global/pm/2012/pm-9-12-baltsens.pdf Swedish Chemicals Agency (KEMI): The BaltSens Project – The sensitivity of the Baltic Sea ecosystems to hazardous compounds]</ref> The shallow [[Sill (geology)|sills]] are obstacles to the flow of heavy salt water from the Kattegat into the basins around [[Bornholm]] and [[Gotland]]. |
|||
The Kattegat and the southwestern Baltic Sea are well oxygenated and have a rich biology. The remainder of the Sea is brackish, poor in oxygen and in species. Thus, statistically, the more of the entrance that is included in its definition, the healthier the Baltic appears; conversely, the more narrowly it is defined, the more endangered its biology appears. |
|||
== Балтичке државе == |
== Балтичке државе == |
||
{{colbegin|4}} |
|||
* {{ДАН}} |
* {{ДАН}} |
||
* {{ЕСТ}} |
* {{ЕСТ}} |
||
| Ред 16: | Ред 38: | ||
* {{ФИН}} |
* {{ФИН}} |
||
* {{ШВЕ}} |
* {{ШВЕ}} |
||
{{colend}} |
|||
== Веће реке == |
== Веће реке == |
||
Најважније реке које се уливају у Балтичко море су: |
Најважније реке које се уливају у Балтичко море су: |
||
{{colbegin|4}} |
|||
* [[Летонија]] |
* [[Летонија]] |
||
** [[Дзвина]] |
** [[Дзвина]] |
||
| Ред 49: | Ред 72: | ||
** [[Гета]] |
** [[Гета]] |
||
** [[Луле]] |
** [[Луле]] |
||
{{colend}} |
|||
== Острва Балтичког мора == |
== Острва Балтичког мора == |
||
| Ред 106: | Ред 130: | ||
| |
| |
||
|} |
|} |
||
== Референце == |
|||
{{reflist|30em}} |
|||
== Литература == |
|||
{{refbegin|30em}} |
|||
* {{cite book|editor-last=Fairbridge |editor-first=Rhodes |title=The Encyclopedia of Oceanography| first=Pentti |last=Alhonen |chapter=Baltic Sea |pages=87–91 |location=New York |publisher=Van Nostrand Reinhold Company |year= 1966}} |
|||
* Aarno Voipio (ed., 1981): "The Baltic Sea." Elsevier Oceanography Series, vol. 30, Elsevier Scientific Publishing, 418 p, {{ISBN|0-444-41884-9}} |
|||
* {{cite journal | last1 = Ojaveer | first1 = H. | last2 = Jaanus | first2 = A. | last3 = MacKenzie | first3 = B. R. | last4 = Martin | first4 = G. | last5 = Olenin | first5 = S. | display-authors = etal | year = 2010 | title = Status of Biodiversity in the Baltic Sea | url = | journal = [[PLoS ONE]] | volume = 5 | issue = 9| page = e12467 | doi = 10.1371/journal.pone.0012467 }} |
|||
*{{cite book|last1=Peter|first1=Bruce|title=Baltic Ferries|date=2009|publisher=Ferry Publications|location=Ramsey, Isle of Man|isbn=9781906608057}} |
|||
*{{cite book|last=The BACC II Author Team |first=, et.al|url=https://link.springer.com/book/10.1007%2F978-3-319-16006-1 |title=Second Assessment of Climate Change for the Baltic Sea Basin |publisher=Springer |year=2015 |isbn= 978-3-319-16006-1 |DOI=10.1007/978-3-319-16006-1}} |
|||
{{refend}} |
|||
== Спољашње везе == |
== Спољашње везе == |
||
{{Commonscat|Baltic Sea}} |
{{Commonscat|Baltic Sea}} |
||
{{AmCyc poster|Baltic Sea}} |
|||
{{EB1911 poster|Baltic Sea}} |
|||
{{refbegin|30em}} |
|||
* -{[https://web.archive.org/web/20160303225024/http://www.smhi.se/sgn0102/n0205/havsomr/havsomr_plansch.pdf The Baltic Sea, Kattegat and Skagerak – sea areas and drainig basins, poster with integral information by the Swedish Meteorological and Hydrological Institute]}- |
|||
* -{[http://www.baltic.vtt.fi/demo/baltmap.htm Baltic Sea clickable map and details.]}- |
|||
* -{[https://web.archive.org/web/20070911174644/http://www.balticsea.lt/en Protect the Baltic Sea while it's still not too late.]}- |
|||
* -{[https://archive.is/20120728165223/http://www.balticseaportal.fi/ The Baltic Sea Portal]}- |
|||
* -{[https://web.archive.org/web/20110625011603/http://www.balticnest.org/ www.balticnest.org]}- |
|||
* -{[https://web.archive.org/web/20050317135023/http://depts.washington.edu/baltic/encyclopedia.html Encyclopedia of Baltic History]}- |
|||
* -{[http://www.abc.se/~pa/uwa/wrecks.htm Old shipwrecks]}- |
|||
* -{[https://web.archive.org/web/20071212134140/http://www.pgi.gov.pl/pgi_en/index.php?option=news&task=viewarticle&sid=4&Itemid=2 How the Baltic Sea was changing]}- |
|||
* -{[http://www.helsinki.fi/maantiede/geofi/fennia/demo/pages/oksanen.htm Late Weichselian and Holocene shore displacement history of the Baltic Sea in Finland]}- |
|||
* -{[http://maps.grida.no/baltic Baltic Environmental Atlas: Interactive map of the Baltic Sea region]}- |
|||
* -{[http://www.spiegel.de/international/europe/0,1518,524139,00.html Can a New Cleanup Plan Save the Sea? – ''spiegel.de'']}- |
|||
* -{[https://web.archive.org/web/20060903112114/http://www.ferrylines.com/en/routes/ferries-in-the-baltic-sea/ List of all ferry lines in the Baltic Sea]}- |
|||
* -{[http://www.helcom.fi/ The Helsinki Commission (HELCOM)]}- |
|||
* -{[http://www.baltice.org/ Baltice.org]}- |
|||
* -{[http://www.balticseawind.org/ Baltic Sea Wind]}- |
|||
* -{[https://web.archive.org/web/20090831081653/http://andreaskiel.blip.tv/file/2323160 Ostseeflug]}- |
|||
{{refend}} |
|||
{{Светско море}} |
{{Светско море}} |
||
{{Authority control}} |
|||
[[Категорија:Балтичко море|*]] |
[[Категорија:Балтичко море|*]] |
||
Верзија на датум 1. новембар 2017. у 16:59

Један корисник управо ради на овом чланку. Молимо остале кориснике да му допусте да заврши са радом. Ако имате коментаре и питања у вези са чланком, користите страницу за разговор.
Хвала на стрпљењу. Када радови буду завршени, овај шаблон ће бити уклоњен. Напомене
|
Балтичко море (краће Балтик), налази се на северу Европе и са Северним морем повезано је тесним мореузима: Сунда, Велики Белт, Мали Белт, Скагерак, Категат и Килским каналом. Назива се и као Источно море и Западно море. Оно запљускује обале Скандинавског полуострва, већег броја земаља источне, северне и централне Европе.[1] Због његове велике површине (422.300 km²) и лоше повезаности са Северним морем-што онемогућава размену воде, а великог прилива слатке воде ово море је једно од мора са најнижим салинитетом на свету.
Највећа дубина Балтичког мора износи 459 m. Велики заливи су: Ботнички залив, Фински залив, Ришки залив, Куронски залив, Гдањски залив, Шћећински залив, Либечки залив и Килски залив.
Дефиниције

Администрација
Хелсиншка конвенција о заштити морске средине подручја Балтичког мора обухвата Балтичко море и Категат, без називања Категата делом Балтичког мора, „За потребе ове конвенције „подручје Балтичког мора” је Балтичко море и улаз у Балтичко море, ограничено паралелом Скава у Скагераку на 57° 44,43'С.”[2]
Историја саобраћаја
Историјски Данско краљевство је наплаћивало бродовим пролаз кроз теснаце на граници између океана и копном окруженог Балтичког мора. Наплата је вршена у Ересунду код Кронборшког дворца у близини Хелсингер, у Великом Белту код Ниборга. У Little Belt, the site of intake was moved to Fredericia, after that stronghold had been built. The narrowest part of Little Belt is the "Middelfart Sund" near Middelfart.[3]
Океанографија
Geographers widely agree that the preferred physical border of the Baltic is a line drawn through the southern Danish islands, Drogden-Sill and Langeland.[4] The Drogden Sill is situated north of Køge Bugt and connects Dragør in the south of Copenhagen to Malmö; it is used by the Øresund Bridge, including the Drogden Tunnel. By this definition, the Danish Straits are part of the entrance, but the Bay of Mecklenburg and the Bay of Kiel are parts of the Baltic Sea. Another usual border is the line between Falsterbo, Sweden and Stevns Klint, Denmark, as this is the southern border of Øresund. It's also the border between the shallow southern Øresund (with a typical depth of 5–10 meters only) and notably deeper water.
Хидрографија и биологија
Drogden Sill (depth of 7 m (23 ft)) sets a limit to Øresund and Darss Sill (depth of 18 m (59 ft)), and a limit to the Belt Sea.[5] The shallow sills are obstacles to the flow of heavy salt water from the Kattegat into the basins around Bornholm and Gotland.
The Kattegat and the southwestern Baltic Sea are well oxygenated and have a rich biology. The remainder of the Sea is brackish, poor in oxygen and in species. Thus, statistically, the more of the entrance that is included in its definition, the healthier the Baltic appears; conversely, the more narrowly it is defined, the more endangered its biology appears.
Балтичке државе
Веће реке
Најважније реке које се уливају у Балтичко море су:
Острва Балтичког мора
| Данска | Немачка | Немачка и Пољска | Пољска | Естонија | Русија | Финска | Шведска |
| Селанд | Ферман | Узедом | Волин | Хијума | Кронштат | Оландска острва | Готланд |
| Фин | Риген | Сарема | Еланд | ||||
| Лоланд | |||||||
| Фалстер | |||||||
| Борнхолм |
Референце
- ^ „Coalition Clean Baltic”. Архивирано из оригинала 2. 6. 2013. г. Приступљено 5. 7. 2013.
- ^ Text of Helsinki Convention
- ^ Pierers Universal-Lexikon, (a German encyclopedia from 1857–1865, automatic transcription of little quality): Sundzoll (Sound Dues )
- ^ Leibniz-Institut für Ostseeforschung Warnemünde: "Gehört das Kattegatt noch zur Ostsee" (Is the Kattegat a part of the Baltic Sea?)
- ^ Swedish Chemicals Agency (KEMI): The BaltSens Project – The sensitivity of the Baltic Sea ecosystems to hazardous compounds
Литература
- Alhonen, Pentti (1966). „Baltic Sea”. Ур.: Fairbridge, Rhodes. The Encyclopedia of Oceanography. New York: Van Nostrand Reinhold Company. стр. 87—91.
- Aarno Voipio (ed., 1981): "The Baltic Sea." Elsevier Oceanography Series, vol. 30, Elsevier Scientific Publishing, 418 p, ISBN 0-444-41884-9
- Ojaveer, H.; Jaanus, A.; MacKenzie, B. R.; Martin, G.; Olenin, S.; et al. (2010). „Status of Biodiversity in the Baltic Sea”. PLoS ONE. 5 (9): e12467. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0012467.
- Peter, Bruce (2009). Baltic Ferries. Ramsey, Isle of Man: Ferry Publications. ISBN 9781906608057.
- The BACC II Author Team, , et.al (2015). Second Assessment of Climate Change for the Baltic Sea Basin. Springer. ISBN 978-3-319-16006-1. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-16006-1.
Спољашње везе
- The Baltic Sea, Kattegat and Skagerak – sea areas and drainig basins, poster with integral information by the Swedish Meteorological and Hydrological Institute
- Baltic Sea clickable map and details.
- Protect the Baltic Sea while it's still not too late.
- The Baltic Sea Portal
- www.balticnest.org
- Encyclopedia of Baltic History
- Old shipwrecks
- How the Baltic Sea was changing
- Late Weichselian and Holocene shore displacement history of the Baltic Sea in Finland
- Baltic Environmental Atlas: Interactive map of the Baltic Sea region
- Can a New Cleanup Plan Save the Sea? – spiegel.de
- List of all ferry lines in the Baltic Sea
- The Helsinki Commission (HELCOM)
- Baltice.org
- Baltic Sea Wind
- Ostseeflug
